C++ Objects and Classes
In object-oriented programming languages like C++, the data and functions (procedures to manipulate the data) are bundled together as a self-contained unit called an object. A class is an extended concept similar to that of structure in C programming language; this class describes the data properties alone. In C++ programming language, class describes both the properties (data) and behaviors (functions) of objects. Classes are not objects, but they are used to instantiate objects.
What is a class?
Primary purpose of a class is to held data/information. This is achieved with attributes which is also know as data members.
The member functions determine the behavior of the class i.e. provide definition for supporting various operations on data held in form of an object.
Definition of a class
Syntax:
Class class_name
{
Data Members;
Methods;
}
Example:
class A
{
public:
double length; // Length of a box
double breadth; // Breadth of a box
double height; // Height of a box
}Class Members
Data and functions are members.
Data Members and methods must be declared within the class definition.
Example:
Class A
{
int i; // i is a data member of class A
int j; // j is a data member of class A
int i; // Error redefinition of i
}
Example:
Class A
{
int i;
int j;
void f (int, int);
int g();
}
f and g are member function of class A. They determine the behavior of the objects of the class A.
Accessing the Data Members
The public data members of objects of a class can be accessed using the direct member access operator (.).
Let us try following example to make the things clear:
Example:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Box
{
public:
double length; // Length of a box
double breadth; // Breadth of a box
double height; // Height of a box
};
int main( )
{
Box Box1; // Declare Box1 of type Box
Box Box2; // Declare Box2 of type Box
double volume = 0.0; // Store the volume of a box here
// box 1 specification
Box1.height = 4.0;
Box1.length = 6.0;
Box1.breadth = 3.0;
// box 2 specification
Box2.height = 10.0;
Box2.length = 12.0;
Box2.breadth = 12.0;
// volume of box 1
volume = Box1.height * Box1.length * Box1.breadth;
cout << "Volume of Box1 : " << volume <<endl;
// volume of box 2
volume = Box2.height * Box2.length * Box2.breadth;
cout << "Volume of Box2 : " << volume <<endl;
return 0;
}
Program Output:
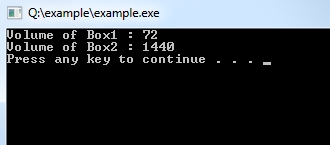
It is important to note that private and protected members can not be accessed directly using direct member access operator (.). We will learn how private and protected members can be accessed.
Program to Enter Students Details and Display it
Example:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class stud
{
public:
char name[30],clas[10];
int rol,age;
void enter()
{
cout<<"Enter Student Name: "; cin>>name;
cout<<"Enter Student Age: "; cin>>age;
cout<<"Enter Student Roll number: "; cin>>rol;
cout<<"Enter Student Class: "; cin>>clas;
}
void display()
{
cout<<"\n Age\tName\tR.No.\tClass";
cout<<"\n"<<age<<"\t"<<name<<"\t"<<rol<<"\t"<<clas;
}
};
int main()
{
class stud s;
s.enter();
s.display();
cin.get(); //use this to wait for a keypress
}
Program Output:
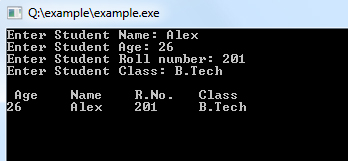

No comments:
Post a Comment